# Customization
This system supports customized development using the Groovy (opens new window) language. Groovy is a superset of the Java language, supporting Java syntax while adding more dynamic features, making it more suitable for domain modeling and runtime enhancement.
TIP
If the team is not familiar with Groovy, they can also develop using pure Java syntax. Groovy has excellent compatibility with Java.
# Target Audience
This document is intended for: developers and implementers of this system
# Structure of Dynamic Logic Definition
Dynamic logic can be maintained through the menu Development Customization -> Dynamic Logic -> Dynamic Logic, with related properties shown in the following image:
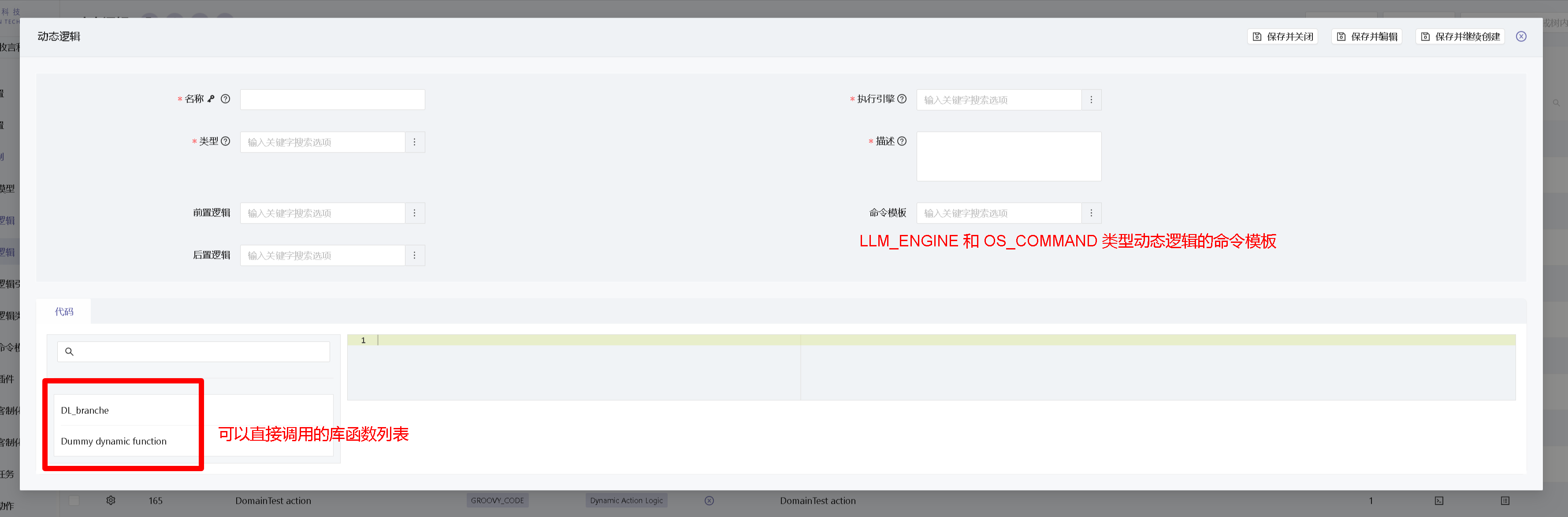
Detailed descriptions of relevant fields are as follows
# Dynamic Logic Engine Overview
The system provides a dynamic logic engine for executing dynamic logic within the system. Dynamic logic can be a piece of Groovy code, an external operating system command, or a call to a large language model, etc.
| Dynamic Logic Engine | Description | preLogic | DynamicPrompt | postLogic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JASPER_REPORT | Used to render Jasper reports to PDF files | Supported | Not Applicable | Supported |
| LLM_ENGINE | Used to request large language models | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| RENDER_LINK | Alias for GROOVY_CODE, returns a link to the caller | Supported | Not Applicable | Supported |
| OS_COMMAND | Used to execute operating system commands | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| GROOVY_CODE | Used to execute Groovy code | Supported | Not Applicable | Supported |
TIP
The name field of dynamic logic-related objects cannot be modified after creation.
# Dynamic Logic Development Guide
# Dynamic Logic Overview
Dynamic logic is a flexible way to implement business logic, allowing developers to define pre-processing logic, post-processing logic, and Prompt templates according to business needs. Through dynamic logic, you can easily implement customization and automation of business processes, improving the flexibility and efficiency of business processing.
# Defining Dynamic Logic
When defining dynamic logic, you need to focus on the following aspects:
- Pre-processing Logic (preLogic): Logic executed before the main business logic, used for data preparation or pre-processing.
- Post-processing Logic (postLogic): Logic executed after the main business logic, used for processing results or performing subsequent operations.
- DynamicPrompt Template: Template used to generate dynamic content, which can be dynamically rendered based on the results of pre-processing logic.
# Parameter Passing and Result Handling
During the execution of dynamic logic, please note the following points:
- Pre-processing Result Passing: The results of pre-processing logic will be passed to subsequent Prompt rendering, main business logic, and post-processing logic.
- Prompt Rendering: The Prompt template will be rendered based on the results of pre-processing logic and other input parameters to generate dynamic content.
- Post-processing Logic Parameters: Post-processing logic will receive the results of the main business logic and other necessary parameters for result processing.
- Returning Results: Finally, the execution results of dynamic logic will be returned to the caller for subsequent business processes or display.
# Accessing previous processing results in postLogic
For LLM type DynamicLogic, after receiving a response from the LLM engine, you can use the following code in the postLogic post-processing logic to retrieve the LLM engine's response text:
// 对于 AI 类型的 DynamicLogic,从 LLM 引擎获取回复后,在 postLogic 后处理逻辑中,可以使用如下的代码,获取 LLM 引擎的回复文本。
// For AI type DynamicLogic, after getting the reply from LLM engine, you can use the following code in the postLogic to get the reply text from LLM engine.
String llmOutput = ((previousLogicResult as Map).get('result') as String)2
# Practical Application Examples
Here are some specific business scenarios and dynamic logic definition examples:
# Automatic Customer Credit Limit Adjustment
Business Scenario: Automatically adjust customer credit limits based on historical transaction records and payment situations.
Dynamic Logic Definition:
- Pre-processing Logic (preLogic): Query customer's historical transaction records, payments, and overdue situations.
- DynamicPrompt: Generate credit limit adjustment suggestions based on query results.
- Post-processing Logic (postLogic): Update customer credit limit based on suggestions and send notifications.
# Intelligent Work Order Assignment
Business Scenario: Automatically assign work orders based on order content and technicians' professional fields.
Dynamic Logic Definition:
- Pre-processing Logic: Extract key information from work orders, query available technicians and their professional fields.
- DynamicPrompt: Generate best match recommendations based on work order information and technicians' expertise.
- Post-processing Logic: Execute work order assignment, update system status, and notify relevant personnel.
# Dynamic Pricing Strategy
Business Scenario: Dynamically adjust product prices based on market demand, inventory status, and competitor prices.
Dynamic Logic Definition:
- Pre-processing Logic: Collect market data, inventory information, and competitor prices.
- DynamicPrompt: Analyze data and generate price adjustment suggestions.
- Post-processing Logic: Update product prices, synchronize to sales systems, and notify relevant departments.
These examples demonstrate how dynamic logic can be applied in different business scenarios, achieving intelligent and automated business processes through flexible pre-processing, DynamicPrompt, and post-processing logic.
The above guide aims to help developers better understand and implement dynamic logic to meet the needs of different business scenarios. In practical applications, customizing and optimizing dynamic logic according to specific business requirements can achieve flexibility and automation of business processes.
# Dynamic Logic Types
The following lists the types of customization logic currently supported in the system and their usage scenarios:
- Library Functions: Functions available for other customization logic to call.
- Dynamic Permissions: Dynamic creation permission judgment, deletion and update permission judgment for objects.
- Form and Field Customization: Field interactions in forms, dropdown options, field hiding and displaying, etc.
- Object Lifecycle Customization: Injection of customization logic before and after object creation, modification, deletion, and access.
- Dynamic Actions: Enabling logic and core logic of dynamic actions.
- Scheduled Tasks: Enabling logic and core logic of scheduled tasks.
- Dashboards: Enabling logic and core logic of dashboards and widgets.
- Filters: Enabling logic and filter condition configuration of filters.
- Dynamic Services: Core logic of dynamic services.
- Dynamic Integration: Enabling logic and core logic of dynamic integration.
The following sections provide detailed explanations of the application of dynamic logic in different business scenarios:
- Dynamic Actions
- Dynamic Configuration
- RPC Service Provision
- Dynamic Styles
- Form Field Customization
- Dynamic Integration
- Object Customization
- Object Permission Control
- Reports and Document Printing
- Scheduled Tasks
# Custom Functions 0.30.0+
Custom functions are user-defined dynamic logic that can be directly called by other dynamic logic.
# Function Call Example
First, we need to define a Function logic type DynamicLogic named Test function
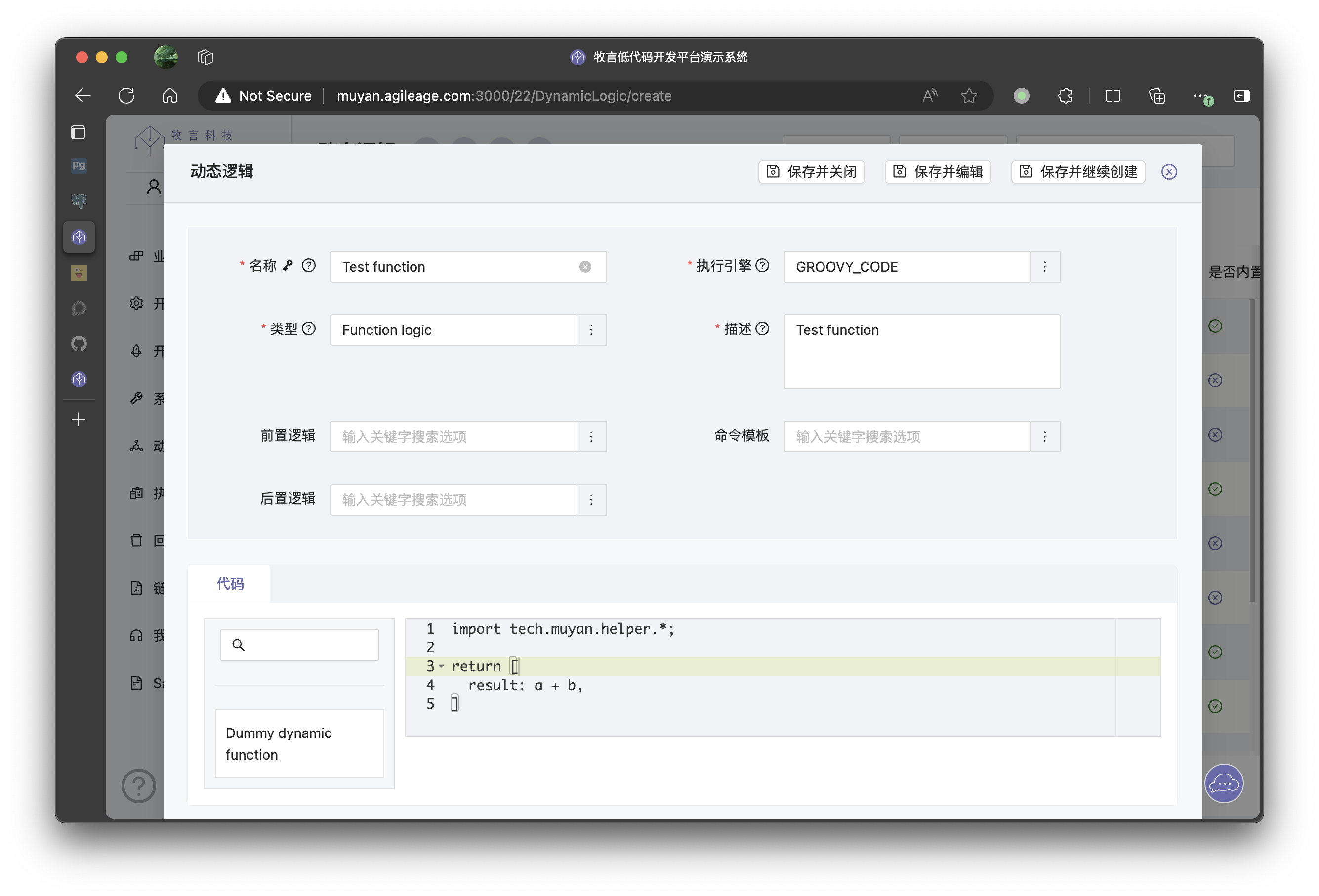
As we can see, our logic is a + b, where a and b are parameters that need to be passed in when calling.
Next, we can call this function in any DynamicLogic. Below is an example using a DynamicAction's CoreLogic
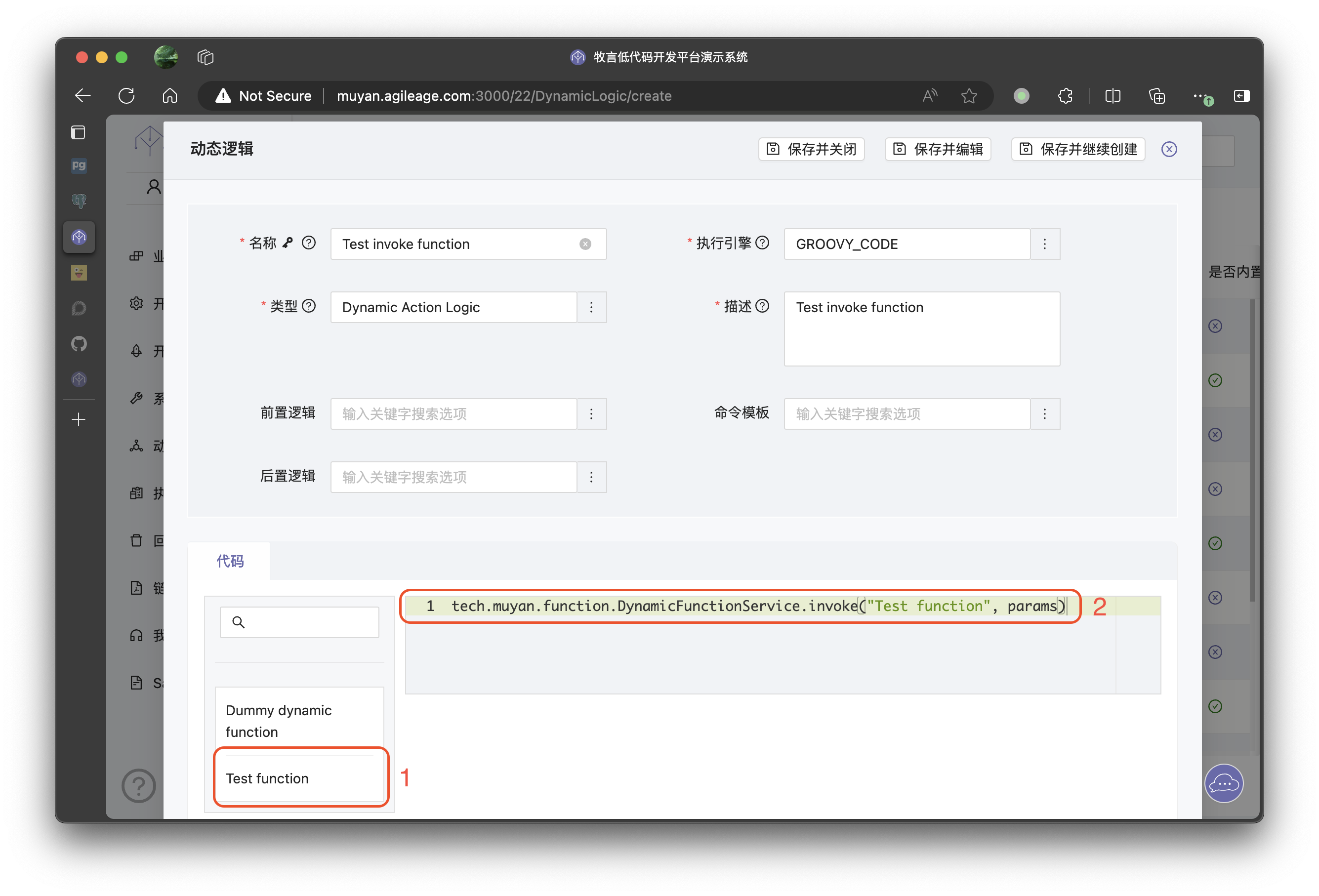
We can see that the Test function1 we just defined appears on the left. After clicking it, the code to call this function will appear in the code editing panel on the right2. The params here is a Map type parameter list. The specific code for calling is:
import tech.muyan.utils.BeanContainer
import tech.muyan.api.DynamicFunctionService
// Define a Map type parameter list
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("a", 1);
params.put("b", 2);
// Call the function we just defined
// The first parameter is the name of DynamicLogic, the second parameter is the input parameters passed during the call, of type Map
// Static method call, DynamicFunctionService is an internal class of the platform, so its definition can't be found in IDE, but it works normally at runtime
tech.muyan.function.DynamicFunctionService.invoke("Test function", params);
// Or use bean method to call
BeanContainer.getBean(DynamicFunctionService.class).invoke("TaskAssignmentLogic", params);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Here we modify it as follows:
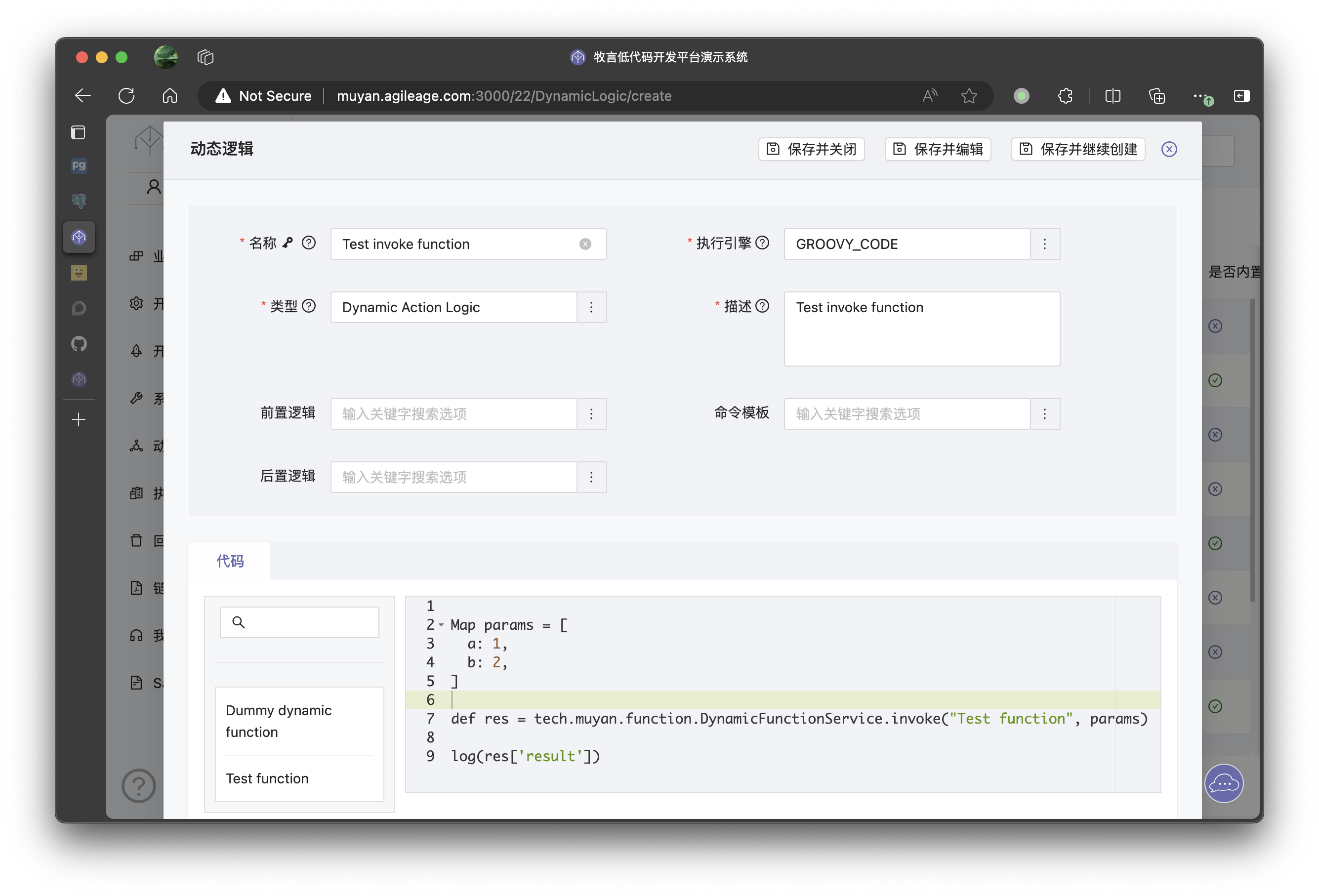
We pass in a and b as 1 and 2 respectively, and then test the execution of this logic (for details on how to call the DynamicAction CoreLogic, please refer to Dynamic Action section). We can see the following results:
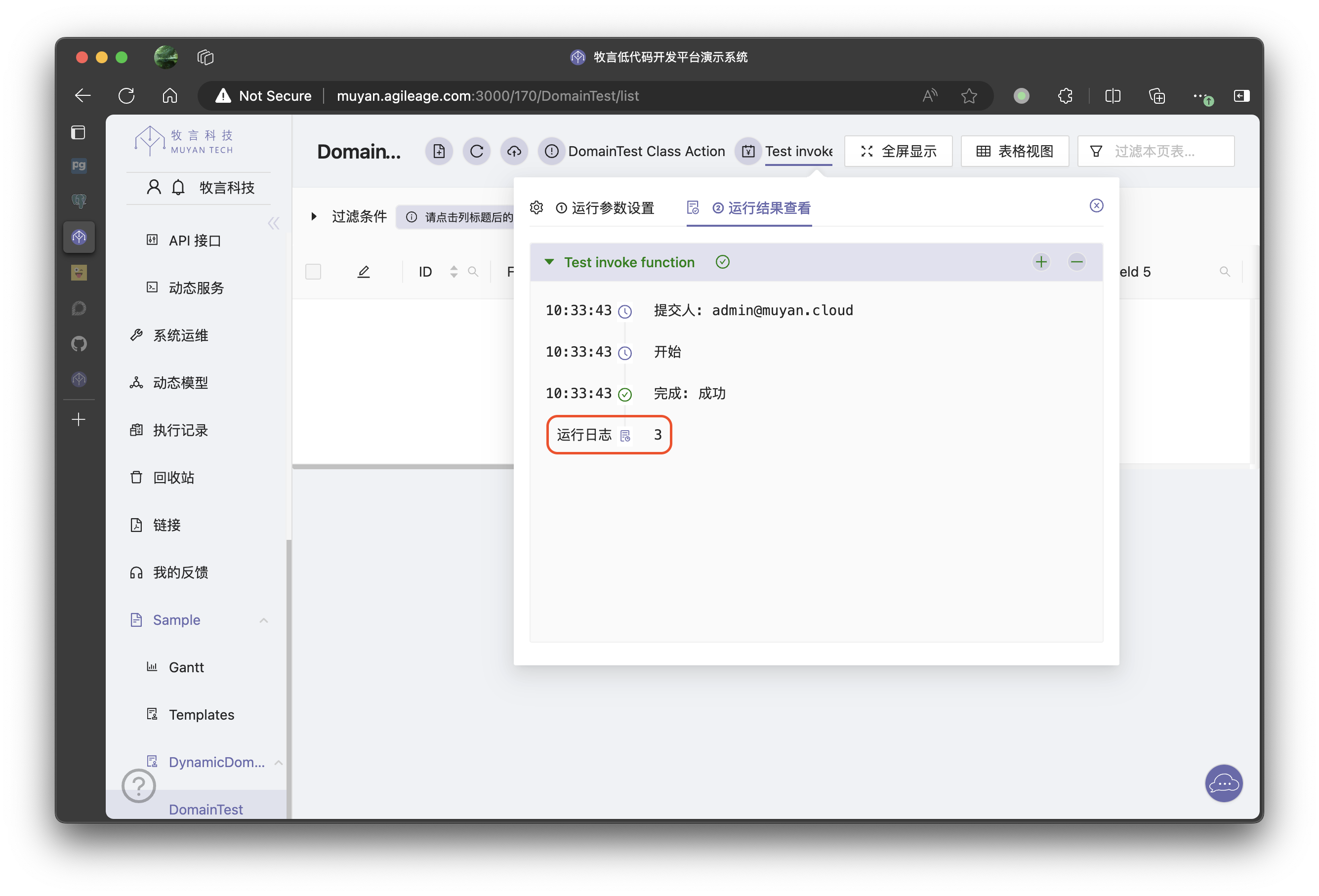
WARNING
The Logic Type of the Dynamic Logic must be Function logic to be invoked by
other Dynamic Logic in the above manner; otherwise, the system will report
follow error: ErrorCode: 15001, ErrorMsg: FunctionNotFound.